I have decided to do it in a kind of squeme to make it more visual and easy to study.
 MECHANISMS: The mechanisms are simply objects that take a concrete force or motion to transform it to a different force or motion.
MECHANISMS: The mechanisms are simply objects that take a concrete force or motion to transform it to a different force or motion.The mechanisms are used to make easier a job.
There are so different types of mechanisms, this are the more used in the mechanisms systems:
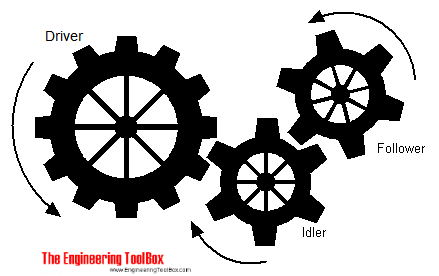
There are different types of gears depending the use (rotary, speed...)
.
- Gears Trains (Rotary motion)
- Rack and Pinion (Type of motion)
- Bevel Gears (Direction of motion)
- CAMS: A cam is a shaped piece of metal or plastic fixed to a rotating shaft. It have different parts:
And there are different types of cams:
EXAMPLE
- Circular cam
- Pear cam
- Snail cam
- Four-lobed cam.
- PULLEYS: Pulleys are used to change the speed, direction of rotation, or turning force or torque. A pulley system consists of two pulley wheels each on a shaft, connected by a belt.
If the pulley wheels are different sizes, the smaller one will spin faster than the larger one. The difference in speed is called the velocity ratio.
MACHINES: Are objects that make it easier to people to do a work.
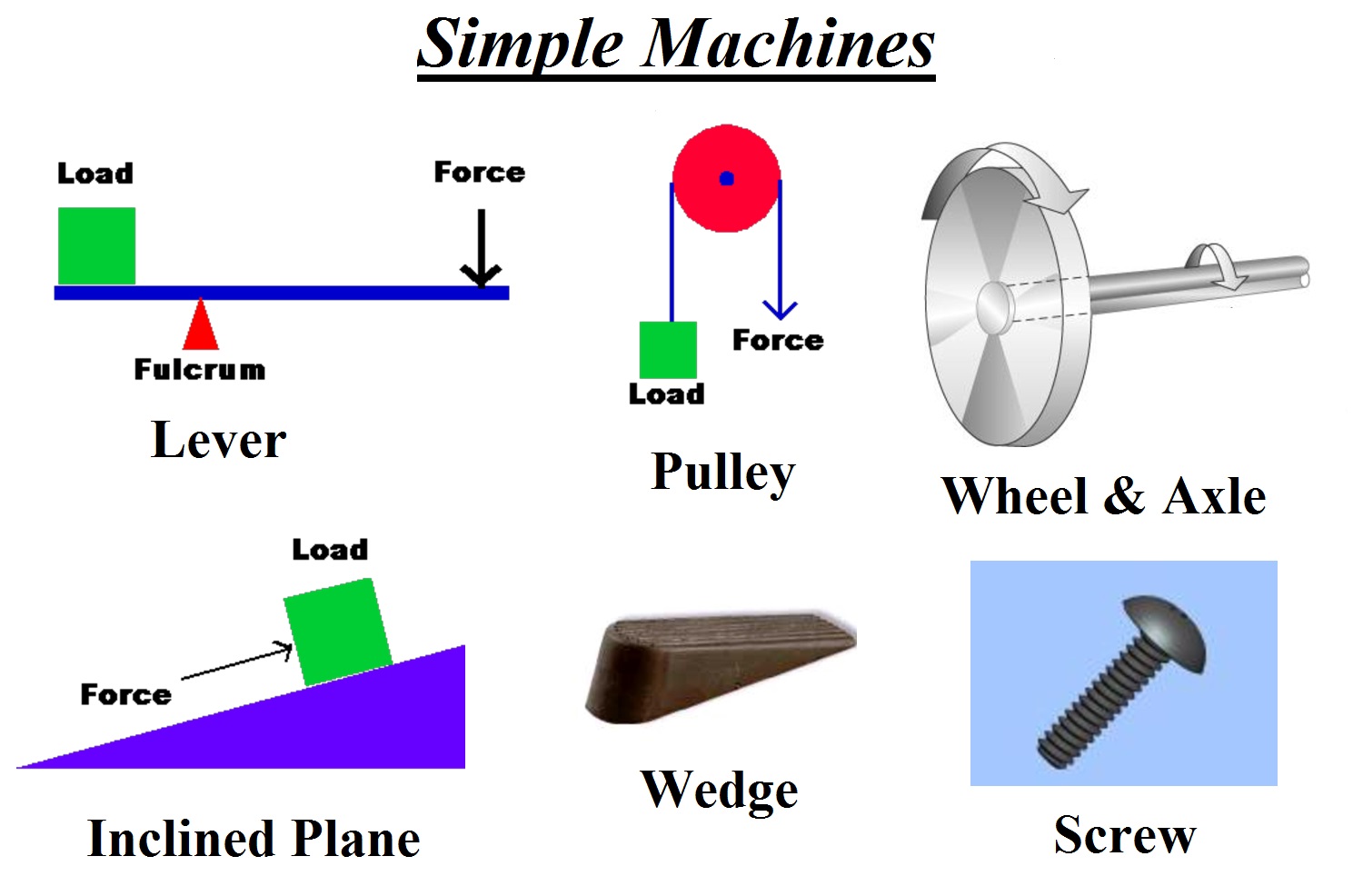
This are the six main types of simple machines:
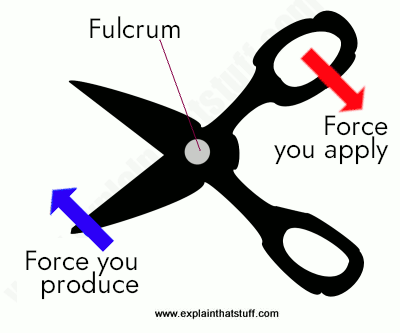
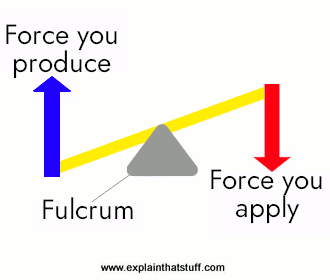
- LEVERS: It is the simplest machine of all. It is a simply bar that helps us to exert a bigger force when you turn it.
Like you can see in the image below it is divided into three main parts: the fulcrum, the effort and the load
Different types of levers:
- Class-1 levers: Is when the force you apply is in the opposite side of the fulcrum of the force you produce. Ex: sccisors
-
- Class-2 levers: This type of lever is putted in an other way: with the fulcrum at the end, the force you produce at the middle and the force you apply at the beggining. Ex: wheelbarrow.

- Class-3 levers: It is different again, in this case we found the fulcrum ata the end and the two forces switch around. Ex: tongs
-

- INCLINED PLANE : An inclined plane is a ramp that assists moving an object up and down heights. This is a plane surface, set at an angle against a orizontal surface.
It works because the greater the distance the smaller the force applied. EX: stairs.

- SCREW: It is a machine that converts rational movement into linear movement. The closer and wider the thereda are (the main part of a screw) stronger will be the hold. It is use to:
- Drill holes
- Hold things together
- Lift heavy objects.
EX: bulb



PULLEY: A basic pulley comprises of a wheel on a fixed axle, with a groove along the edges to guide a rope. Each time the rope wraps around the wheels, you create more lifting power or mechanical advantage. EX: Crane

- WHEEL AND AXEL: Is a simple machine used to move heavy objects in an easiest way. In this simple machine, a wheel is locked to a central axle and they rotate each other when a force is applied on either one of them. Is one of the more used machines. EX: wheel

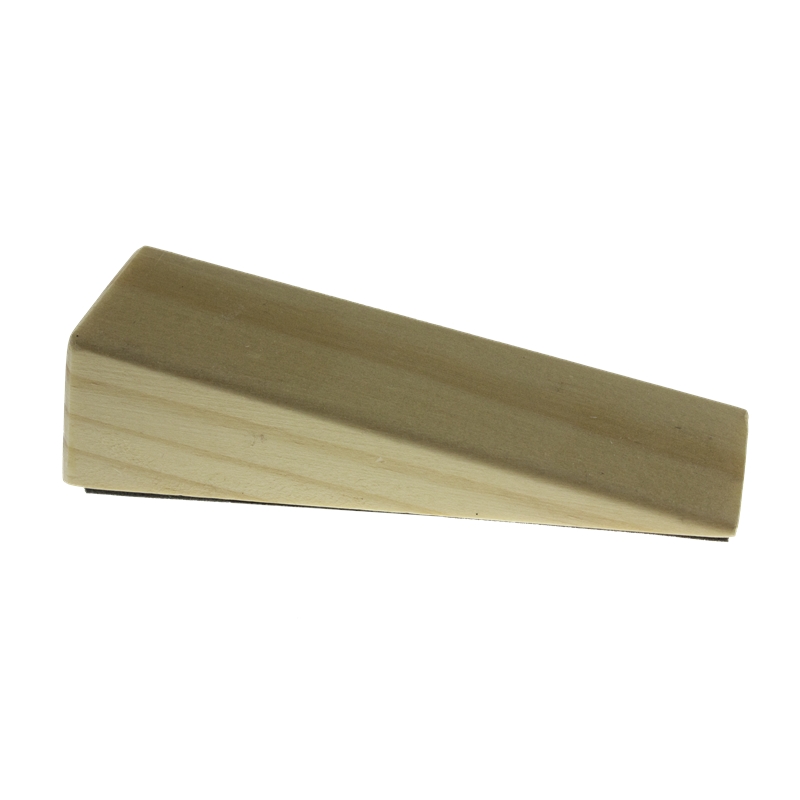
- WEDGE: A wedge is made up of two inclined planes, that meet and form a sharp edge. They don't work without movement. EX: knife, saw...


- Linear motion is moving in a straight line, such as on a paper trimmer.
- Reciprocating motion is moving backwards and forwards in a straight line, as in cutting with a saw.
- Oscillating motion is swinging from side to side, like a pendulum in a clock.
Here you have a mindmap of all the unit:
Personal interests: like I had said in other posts I love dance, and I constantly use gears (the ones that are inside the music tower) and wheels and axels (the ones that are used to move the bar).

http://www.explainthatstuff.com/toolsmachines.html
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/design/systemscontrol/mechanismsrev8.shtml
https://youtu.be/UtfVZtuyuHU
http://aulavirtual.caib.es/c07006305/pluginfile.php/9582/mod_resource/content/1/SCAN-348.pdf
ALL FOTOS: GOOGLE IMAGES.










No comments:
Post a Comment